Master Python programming for beginners with real-world examples, step-by-step tutorials, and proven career paths
Table of Contents
Python programming for beginners has never been more accessible or valuable. If you’re wondering how Instagram processes millions of photos daily, how Netflix predicts your next favorite show, or how self-driving cars navigate streets, the answer is Python.
Learning Python programming for beginners opens doors to incredible career opportunities. From web development to artificial intelligence, Python powers the applications shaping our digital world.
This comprehensive guide covers everything about Python programming for beginners—from basic concepts to real-world applications. Whether you’re starting your coding journey or switching careers, you’ll discover why Python is the perfect first programming language.
Ready to transform your future? Let’s explore Python programming for beginners and unlock your potential.
What is Python Programming for Beginners?
Python programming for beginners starts with understanding what makes this language special. Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language created by Guido van Rossum in 1991.
Think of Python programming for beginners as learning to communicate with computers using simple, English-like commands. Unlike complex languages requiring extensive technical knowledge, Python was designed specifically to be beginner-friendly.
According to Stack Overflow’s Developer Survey, Python consistently ranks as one of the most loved and wanted programming languages globally.
Why Python Programming for Beginners is Perfect for You
Python programming for beginners succeeds because it removes common barriers. The syntax reads like natural language, making code intuitive and easy to understand.
Compare these examples:
# Python programming for beginners – Simple voting check
age = 18
if age >= 18:
print("You can vote!")# Clean, readable Python code
This simplicity makes Python programming for beginners the fastest path to creating real applications. You’ll write functional programs within your first week.
Key Features of Python Programming for Beginners
Understanding these features helps you appreciate why Python programming for beginners is so effective:
- Simple Syntax: Python programming for beginners uses indentation instead of brackets, forcing clean code
- Dynamic Typing: No need to declare variable types—Python figures it out automatically
- Interpreted Language: Run code line-by-line and see instant results
- Extensive Libraries: Over 400,000 packages for any task imaginable
- Cross-Platform: Works on Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile devices
Learn more about Python’s evolution at the official Python documentation.
Why Choose Python Programming for Beginners in 2025?
The job market for Python programming for beginners has exploded. Companies desperately need Python developers across every industry.
Career Opportunities in Python Programming for Beginners
Starting with Python programming for beginners leads to lucrative career paths. According to Indeed’s salary data, Python developers earn impressive salaries:
- Entry-level Python developers: $75,000 – $95,000/year
- Mid-level Python developers: $110,000 – $140,000/year
- Senior Python developers: $140,000 – $180,000/year
- Machine learning engineers: $150,000 – $250,000+/year
These numbers prove Python programming for beginners is a smart investment. Within months of learning, you can start applying for entry-level positions.
Real Success Story: Python Programming for Beginners Works
Sarah’s Journey: Sarah, a 32-year-old marketing manager, started learning Python programming for beginners through free online courses. With zero coding experience, she dedicated 2 hours daily to practice.
After 3 months, Sarah automated her company’s weekly reporting, saving 12 hours weekly. Six months later, she transitioned to a data analyst role with a 45% salary increase. Today, she mentors others starting their Python programming for beginners journey.
Stories like Sarah’s prove that Python programming for beginners transforms careers regardless of your background.
Real-World Applications of Python Programming for Beginners
Python programming for beginners isn’t just theory—it powers the applications you use daily. Let’s explore where Python makes an impact.
Web Development with Python Programming for Beginners
Python programming for beginners excels in web development. Frameworks like Django and Flask make building websites straightforward.
Instagram’s Success Story:
Instagram, serving 2 billion+ users, runs on Django (Python framework). Every photo upload, like, and comment is processed through Python code. This demonstrates that Python programming for beginners can scale to massive applications.
Simple Flask Web App:
# Python programming for beginners – Basic web app
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home():
return 'Hello, World!'This simple example shows how Python programming for beginners can create functional web applications quickly.
Data Science: Python Programming for Beginners’ Biggest Win
Python programming for beginners dominates data science. Libraries like pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib turn complex data analysis into simple tasks.
Netflix Recommendation Engine:
Netflix uses Python programming to analyze viewing patterns from 230+ million subscribers. Their recommendation algorithm, built with Python, drives 80% of content watched. This directly increases customer satisfaction and retention.
Explore data science careers at Kaggle’s learning platform.
Data Analysis Example:
# Python programming for beginners – Sales analysis
import pandas as pd
sales = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
monthly_revenue = sales.groupby('month')['revenue'].sum()
print(monthly_revenue)
# data.csv
month,revenue
Jan,1000
Jan,1500
Feb,2000
Feb,500
Mar,1200
Mar,800
Apr,900:~/chatboat_gen$ streamlit run dataobject.py
Output:
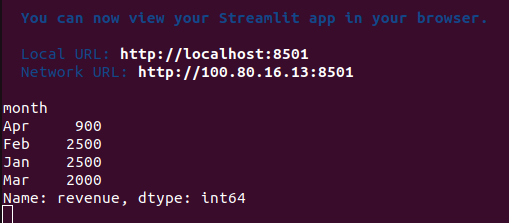
This Python programming for beginners code analyzes millions of records in seconds—a task that takes hours manually.
Artificial Intelligence: The Future of Python Programming for Beginners
Python programming for beginners provides the easiest entry into AI and machine learning. Libraries like TensorFlow and scikit-learn make complex algorithms accessible.
Tesla’s Autopilot:
Tesla uses Python programming to train neural networks powering Autopilot. These AI systems process camera, radar, and sensor data for real-time driving decisions. The same Python programming for beginners techniques Tesla uses are available to anyone learning the language.
Learn AI fundamentals at Google’s Machine Learning Crash Course.
Simple ML Example:
# Here’s a tiny, beginner-friendly spam detector using your emails list and showing the actual output you’d see.
# Simple spam detector with Naive Bayes
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
# 1. Training data (your example)
emails = ['Win money!', 'Meeting at 3pm']
labels = ['spam', 'not spam'] # targets for each email
# 2. Turn text into numbers (bag-of-words)
vectorizer = CountVectorizer()
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(emails) # learn vocabulary + transform
# 3. Train the Naive Bayes model
model = MultinomialNB()
model.fit(X, labels)
# 4. Try the model on new emails
new_emails = [
'Win cash now!',
'See you at the 3pm meeting',
'Win money and free prizes',
]
X_new = vectorizer.transform(new_emails)
predictions = model.predict(X_new)
# 5. Show results
for email, pred in zip(new_emails, predictions):
print(f'"{email}" -> {pred}')Example output
"Win cash now!" -> spam
"See you at the 3pm meeting" -> not spam
"Win money and free prizes" -> spam
What’s happening:
CountVectorizer() converts the email text into a matrix of word counts.
MultinomialNB() learns which words are more common in spam vs not spam based on your labeled examples.
model.predict(...) then guesses the label (spam / not spam) for each new email.
This basic Python programming for beginners code creates a spam filter—the same technology Gmail uses!
Automation: Python Saves Time
Python program excels at automating repetitive tasks. From file management to web scraping, Python handles tedious work automatically.
Google’s Automation:
Google engineers use Python programming extensively for automation. Testing, deployment, and server management all run through Python scripts, allowing small teams to manage massive infrastructure.
Practical Automation Examples:
- Send automated email reports to clients
- Download and organize files automatically
- Generate weekly reports from spreadsheets
- Monitor websites for price changes
Getting Started with Python
Ready to begin your Python journey? Here’s your step-by-step roadmap to success.
Step 1: Install Python
Starting Python requires installing Python on your computer. Visit python.org/downloads and download the latest version (currently Python 3.12).
Installation Steps:
- Download Python installer for your operating system
- Run installer and check ‘Add Python to PATH’
- Verify installation by typing ‘python –version’ in terminal
- Install a code editor like VS Code or PyCharm
Step 2: Your First Python Code
Every Python programmer’s journey starts with ‘Hello, World!’ This traditional first program confirms your setup works correctly.
# Your first Python code
print('Hello, World!')Type this into your code editor, save as ‘hello.py’, and run it. Congratulations—you’ve written your first Python program!
Step 3: Learning Resources for Python
Quality resources accelerate your Python journey. Here are proven learning paths:
Free Resources:
- Python.org Official Tutorial – Comprehensive beginner guide
- Codecademy Python Course – Interactive learning
- freeCodeCamp Python – Project-based learning
- Real Python Tutorials – In-depth articles and videos
Step 4: Practice Projects for Python Programming for Beginners
Theory alone won’t make you proficient. Python programming for beginners requires hands-on practice with real projects.
Beginner Project Ideas:
- Calculator App: Build a basic calculator with addition, subtraction, multiplication, division
- To-Do List: Create a command-line task manager
- Weather App: Fetch weather data from an API
- Password Generator: Create secure random passwords
- Web Scraper: Extract data from websites automatically
Find project ideas at GitHub Python Projects.
Common Mistakes in Python Programming
Learning Python programming involves making mistakes—that’s normal! Avoid these common pitfalls to accelerate your progress.
Mistake 1: Not Practicing Regularly
To be an expert requires consistent practice. Coding 30 minutes daily beats 5-hour weekend sessions. Your brain needs regular exposure to retain programming concepts.
Solution: Set a daily coding schedule. Use apps like HabitTracker to maintain consistency. Join coding challenges on platforms like LeetCode or HackerRank.
Mistake 2: Tutorial Hell
A lot of enthusiasm gets stuck watching endless tutorials without building anything. You can’t learn swimming by watching videos—you must get in the water!
Solution: Follow the 70/30 rule: 70% hands-on coding, 30% learning theory. After each tutorial section, build something related before moving forward.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Error Messages
Python programmer often skips reading error messages. These messages are your friends—they tell you exactly what’s wrong!
Solution: When you see an error, read the entire message. Google the error text. Learn to debug systematically rather than randomly changing code.
Career Paths After Python Programming
Completing Python programming opens multiple career doors. Let’s explore the most popular paths and their requirements.
Python Web Developer
Python web developers build websites and web applications. After mastering Python programming, you’ll learn Django or Flask frameworks.
Required Skills:
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript basics
- Django or Flask framework
- Database knowledge (SQL, PostgreSQL)
- API development and integration
Timeline: 6-9 months from Python programming for beginners to job-ready
Data Analyst/Data Scientist
Data professionals analyze data to extract business insights. Python programming provides the foundation for this high-demand career.
Required Skills:
- pandas and NumPy libraries
- Data visualization (Matplotlib, Seaborn)
- Statistics and probability
- SQL for database queries
Timeline: 8-12 months from Python programming for beginners to an entry-level position
Machine Learning Engineer
ML engineers build AI systems and predictive models. This advanced career builds on Python programming for beginners’ fundamentals.
Required Skills:
- TensorFlow or PyTorch frameworks
- Advanced mathematics (linear algebra, calculus)
- scikit-learn library
- Deep learning concepts
Timeline: 12-18 months from Python programming for beginners to junior ML engineer
Conclusion: Start Your Python Programming for Beginners Journey Today
Python programming for beginners isn’t just learning syntax—it’s unlocking your potential. Whether you dream of building websites, analyzing data, or creating AI systems, Python provides the foundation.
The journey from beginner to a professional developer is challenging but achievable. Thousands have walked this path successfully. With dedication, consistent practice, and the right resources, you’ll join their ranks.
Remember Sarah’s story? She started exactly where you are now—zero coding experience, full of doubts. Today, she’s thriving in her tech career. The difference between her success and staying stuck was taking the first step.
Your Action Plan:
- Install Python today (don’t wait!)
- Complete your first ‘Hello, World!’ program
- Choose one learning resource and commit to it
- Code for 30 minutes daily—no exceptions
- Build your first project within 2 weeks
The tech industry needs more Python developers. Companies are hiring, salaries are competitive, and opportunities are growing. Python programming gives you the ticket to this exciting future.
Every expert was once a beginner. Every impressive application started with someone typing their first line of code. Make today that day. Your Python programming journey starts now.
Need help on your journey? Drop a comment below or check our [Python Beginner Roadmap:Top Python Libraries 2025: The Tools Powering AI, Data, Automation & More] for step-by-step guidance. Let’s code your future together!